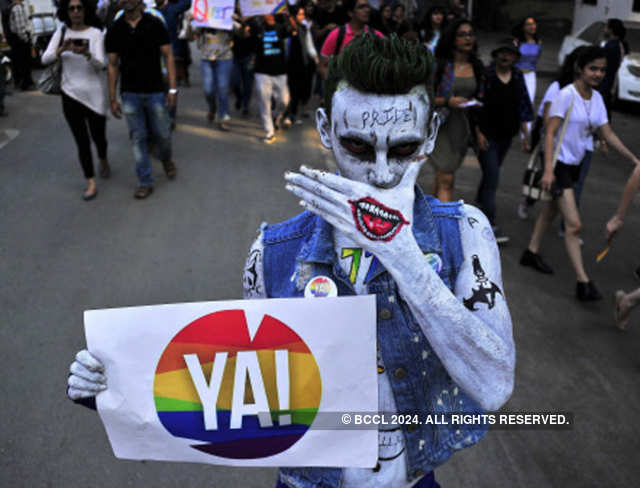

What is "Section 377"?
Section 377 refers to 'unnatural offences' and says whoever voluntarily has carnal intercourse against the order of nature with any man, woman or animal, shall be punished with imprisonment for life, or with imprisonment of either description for a term which may extend to 10 years, and shall also be liable to pay a fine. In pic: A participant from the LGBT community, “shackled” by section 377 of the Indian Penal Code, makes a silent appeal to decriminalise homosexuality in India
1/6
BCCL
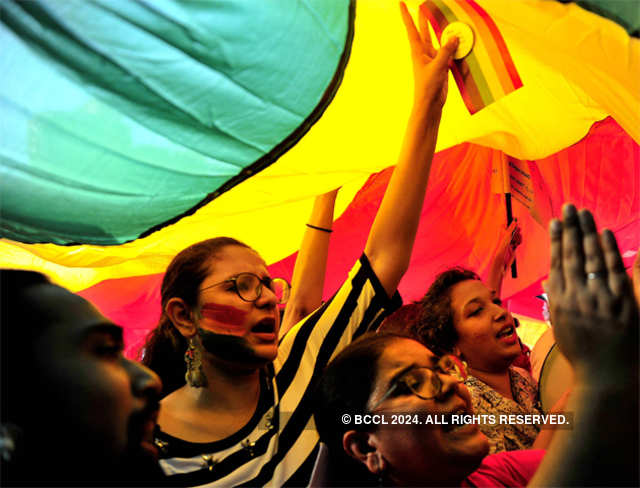
India's take on Section 377
Gay sex has long been taboo in conservative India, particularly in rural areas where nearly 70 percent of people live, with homophobia widespread. Some still regarding homosexuality as a mental illness. Hindu right-wing groups supportive of Prime Minister Narendra Modi's ruling Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) have been especially vocal, calling gay relationships a disease and a Western cultural import. Ahead of the Supreme Court hearing on petitions filed against Section 377 of the Indian Penal Code, Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) leader Subramanian Swamy on Tuesday opined that homosexuality was a danger to national security.
2/6
BCCL
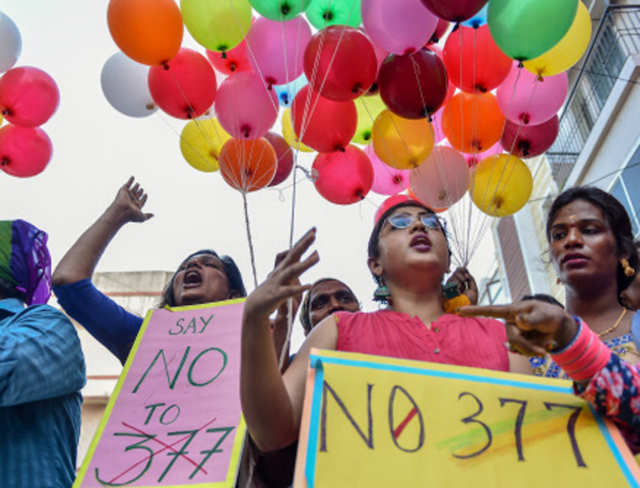
Is 'Section 377' legitimate?
Coming from different parts of the country with diverse religion, age, sex and other backgrounds, the petitioners said that section 377 legitimises the stigma associated with sexual orientation and its expression something which is essential, fundamental, intrinsic and innate to an individual. In pic: LGBT community members participate in 'National Coming Out Day' to mark the anniversary of High Court's verdict amending Section 377, in Chennai.
3/6
PTI
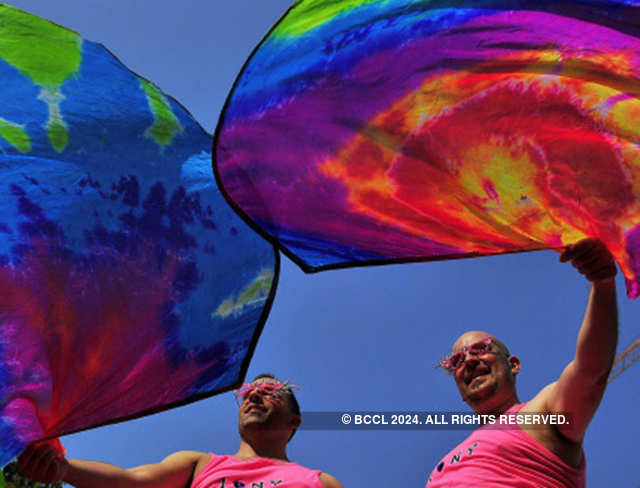

Talks but no action?
June is celebrated worldwide as the Pride Month, but the community members and activists feel that the month's significance is limited to marches and panel discussions without any concrete steps on the ground. LGBTQ activist Mohnish Malhotra, who has been organising Pride Parade in the city, said violent incidents against the community members have become a common sight.
4/6
BCCL
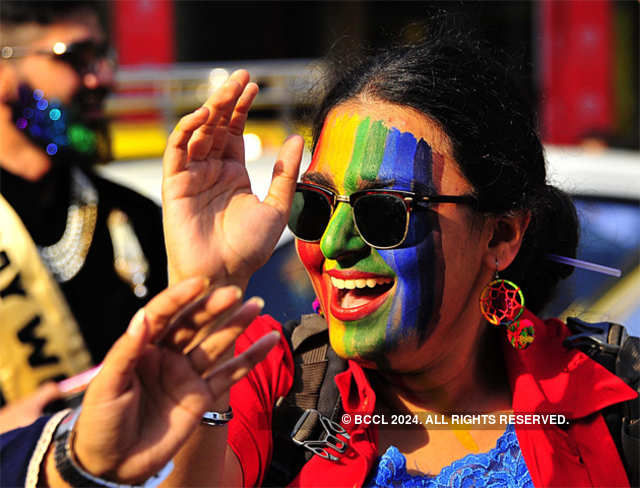

Need of the hour to acknowledge LGBTQ community
Activists feel that the community has to face homophobia on a daily basis, with people refusing accommodation and other basic needs to the LGBTQ members. "The LGBTQ members have to keep their sexual preferences hidden so that they are able to live a normal life," said lawyer-activist Anand Grover, who is a founder-member of Lawyers Collective. "The mindset of the people can only be changed through interaction with the community. The only way we can move forward is when we remove the tag of 'criminals' by curbing section 377 of IPC," he said.
5/6
BCCL
Homosexuality: Not an illness
The Indian Psychiatric Society (IPS) had recently said that homosexuality was still viewed as a mental illness. "We founded a taskforce last year for dealing with queer issues. We had said that homosexuality is not a mental illness," IPS president Ajit V Bhide said, adding that section 377 needed to be amended.
No comments:
Post a Comment